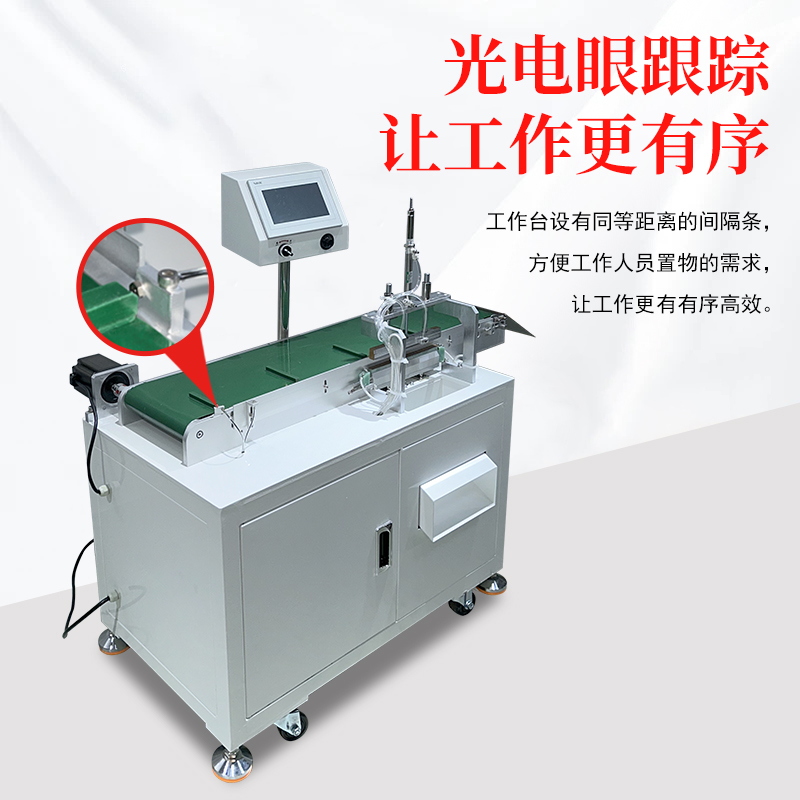
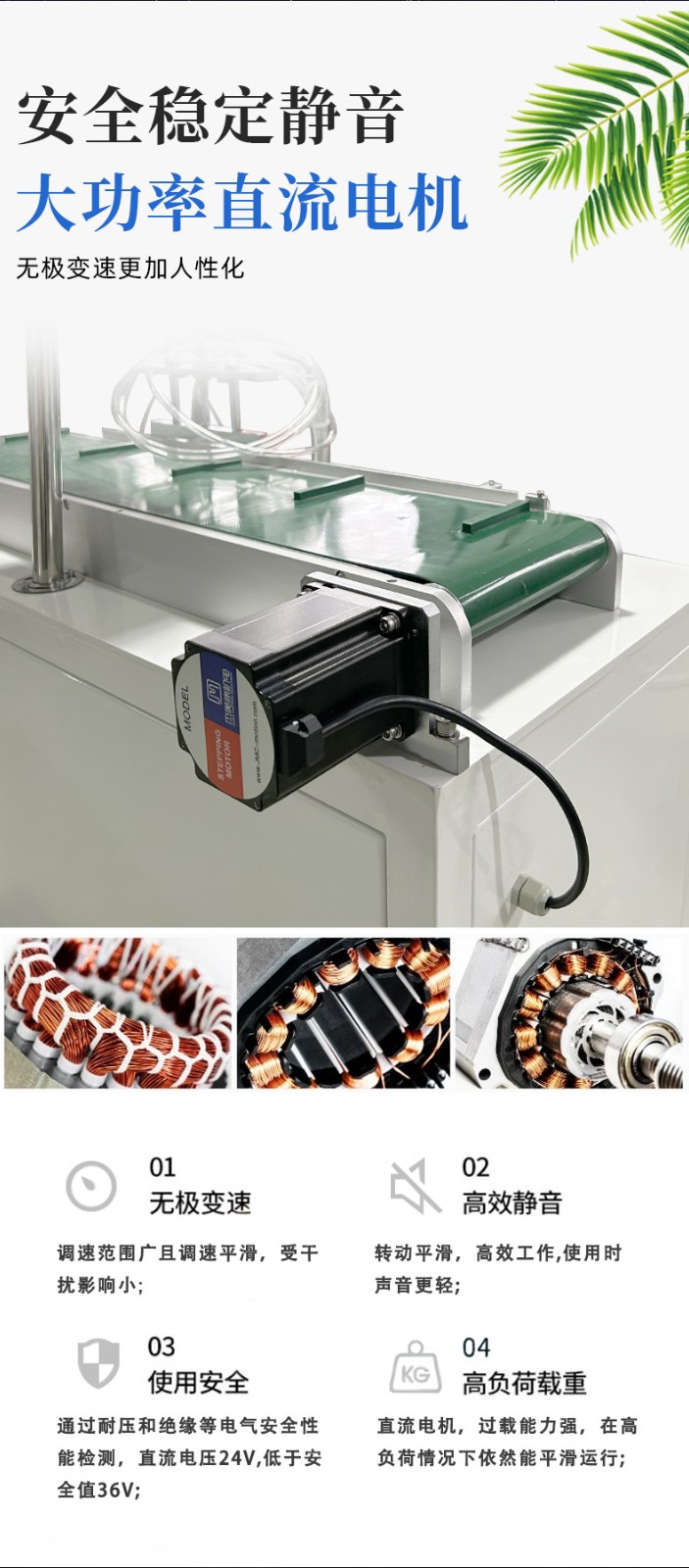
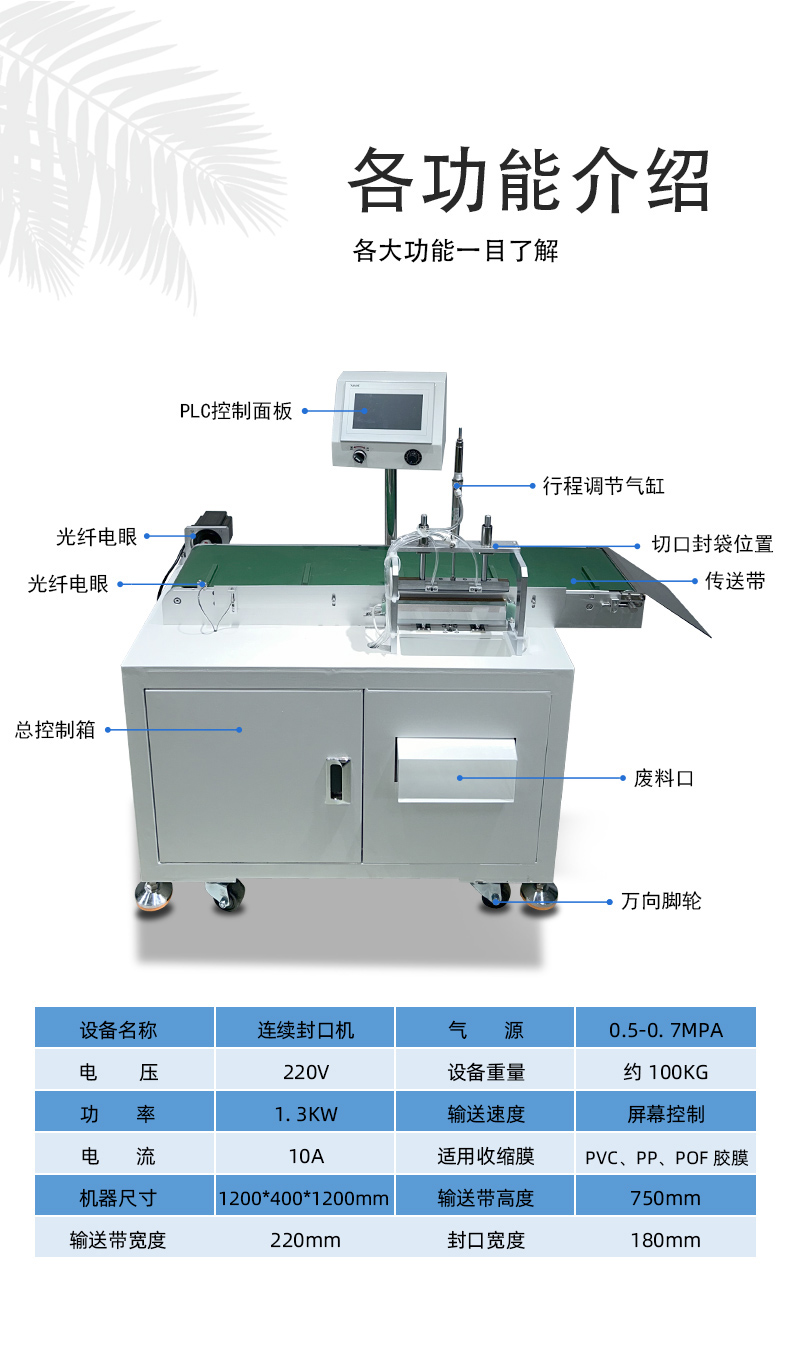
During long-term use, continuous pneumatic sealing machines may encounter various malfunctions due to component wear, improper operation, or inadequate maintenance. The following are common faults and their corresponding solutions to help quickly identify and resolve issues:
This is one of the most common faults, mainly characterized by easy cracking, gaps at the sealed area, or even leakage of contents.
Possible Causes:
- Insufficient heating temperature: The set temperature is too low to fully melt the packaging material.
- Inadequate sealing pressure: Insufficient pressure in the pneumatic system results in inadequate compression of the material by the sealing strips.
- Excessively short sealing time: Heating stops before the material is fully fused.
- Damaged heating elements: Such as broken heating wires or partial failure of the heating plate to generate heat.
- Mismatched packaging materials: Use of non-thermoplastic materials (e.g., uncoated paper) or materials thicker than the equipment's applicable range.
Solutions:
- Gradually increase the heating temperature (adjust by 5-10℃ each time) and test the sealing effect until it is secure.
- Check if the air compressor pressure meets the standard (usually 0.4-0.6MPa for equipment). Adjust the pneumatic valve to increase pressure; if the pressure is unstable, inspect for air leaks in the pipes or blockages in the solenoid valve.
- Slow down the conveyor belt speed to extend the sealing time (adjust the conveying frequency via the control panel).
- Power off and inspect the heating elements; replace broken heating wires or damaged heating plates. 同时,检查温度传感器,确保温度反馈准确。
- Replace with thermoplastic packaging materials suitable for the equipment, or adjust the temperature and pressure according to material thickness (thicker materials require higher temperature and pressure).
The sealed surface is uneven, with wrinkles or local shrinkage and scorching of the material, affecting sealing performance and appearance.
Possible Causes:
- Excessively high heating temperature: Causes over-melting and shrinkage of the material.
- Uneven sealing pressure: Inconsistent pressure at both ends of the sealing strips or uneven surface of the strips.
- Unstable conveyor belt operation: Fluctuating conveying speed or belt deviation leads to uneven material stress.
- Contaminated or worn sealing strips: Oil, impurities on the strip surface, or scratches and deformation due to long-term use.
Solutions:
- Reduce the heating temperature and observe if the seal is flat (immediately lower the temperature if scorching odor occurs due to overheating).
- Adjust the pressure balance valve of the pneumatic system to ensure uniform pressure at both ends of the sealing strips; check if the strips are deformed, and replace with new ones and calibrate levelness if necessary.
- Inspect the conveyor belt drive motor for normal operation and adjust the tightness of the drive chain; if the belt deviates, adjust the tension wheels at both ends to correct the conveying direction.
- Power off and clean the strip surface with alcohol to remove oil and impurities; if the strips are severely worn, replace them directly (high-temperature resistant and wear-resistant materials such as Teflon-coated strips are recommended).
The pneumatic system is the core power source, and malfunctions can prevent the sealing machine from pressing or operating normally.
Possible Causes:
- Insufficient air supply pressure: Air compressor not started, low pressure in the air storage tank, or blocked/leaking air pipes.
- Solenoid valve failure: Burned coil or stuck valve core, preventing normal air circuit on/off.
- Cylinder damage: Aging or leaking piston seals, or stuck piston rod.
Solutions:
- Check the air compressor operation to ensure the air storage tank pressure meets equipment requirements (0.4-0.6MPa); inspect for loose pipe joints, apply soapy water to joints—bubbles indicate leaks, requiring tightening or replacement of joints; clean impurities in the pipes (by disconnecting and blowing through the pipes).
- Power off and test the solenoid valve coil resistance (normally about several tens of ohms); if resistance is infinite, the coil is burned and needs replacement; if the valve core is stuck, disassemble and clean with alcohol before reassembling (ensure power is off during operation).
- Check for cylinder leaks (obvious air flow sound at the piston rod); replace piston seals if leaking; if the rod is stuck, inspect for foreign objects or apply dedicated pneumatic lubricant to reduce friction.
The conveyor belt is critical for continuous operation, and malfunctions can cause production interruptions.
Possible Causes:
- Drive motor failure: Motor not starting (e.g., no power supply, burned motor) or abnormal speed.
- Transmission system issues: Loose/broken drive chain/belt or poor gear engagement.
- Control system failure: Abnormal output signals from PLC or microcomputer controller fail to drive the conveyor motor.
Solutions:
- Check if the motor power is connected (measure voltage with a multimeter); if power is normal but the motor does not run, it may be burned and needs replacement; if the motor makes abnormal noise or runs slowly, bearings may be worn and require repair or replacement.
- Power off and inspect the drive chain/belt; adjust tensioning devices if loose, or replace with new ones if broken; clean impurities between gears to ensure smooth engagement.
- Check the output terminals of the control system; if no signal is output, the controller may be faulty—contact the manufacturer for repair or replace the control module.
Loss of temperature control directly affects sealing quality and may even damage the equipment.
Possible Causes:
- Damaged heating elements: Broken heating wires or poor contact of the heating plate prevent heating.
- Temperature controller failure: Abnormal display on the thermostat or incorrect output signals (e.g., continuous heating).
- Thermocouple (temperature sensor) failure: Broken or poorly connected thermocouple fails to feed back actual temperature, causing misjudgment by the controller.