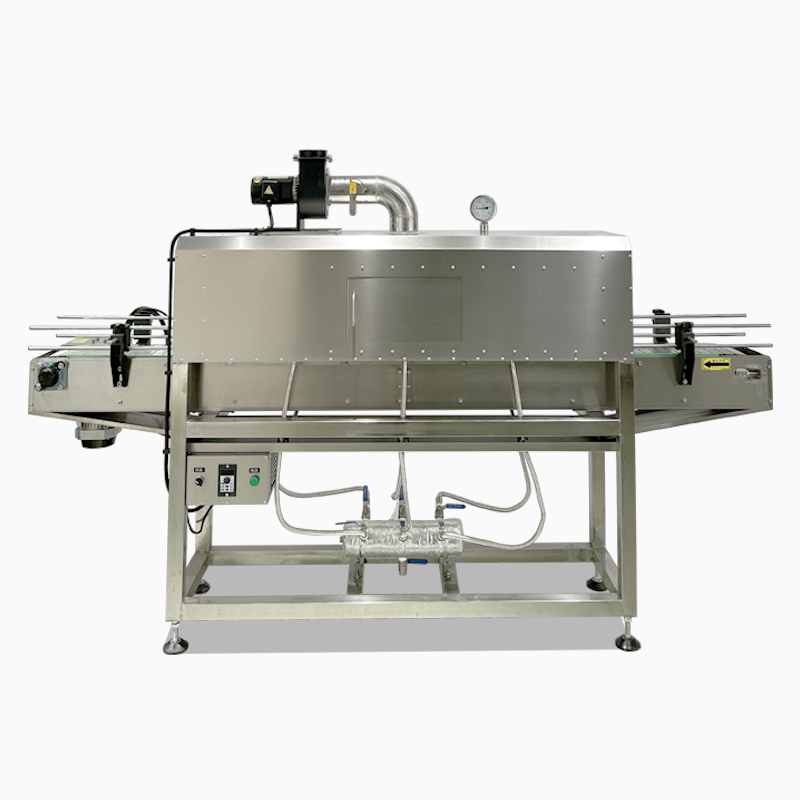
The material of the shrink film is a core factor affecting the shrinking effect. Differences in properties such as molecular structure, heat resistance, and ductility of different materials directly lead to variations in key indicators like shrinkage temperature, shrinkage rate, fit, and transparency. Below, starting from the characteristics of common materials, we will analyze their specific impacts on the shrinking effect in detail:
Currently, mainstream shrink film materials on the market include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), POF (polyolefin), PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), etc. The differences in their shrinking effects are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- Shrinkage Temperature: Relatively low, usually starting to shrink at 60-90℃, suitable for heat-sensitive products (such as some foods and cosmetics).
- Shrinkage Rate: The longitudinal shrinkage rate is about 10%-30%, and the transverse shrinkage rate is about 40%-60%. The shrinkage unevenness is obvious (transverse shrinkage is stronger), which may cause wrinkles at the packaging edges.
- Fit: The fit after shrinkage is moderate, but if the product has a complex shape (such as with many edges and corners), it is prone to local looseness.
- Transparency: High transparency, but long-term storage may cause yellowing due to plasticizer migration, affecting the appearance.
- Limitations: Poor environmental friendliness (contains chlorine), easy to embrittle at low temperatures, insufficient toughness after shrinkage, not suitable for packaging heavy or sharp products.
- Shrinkage Temperature: Moderate, generally 80-120℃, with a wide heating range, and lower requirements for equipment temperature control.
- Shrinkage Rate: The longitudinal and transverse shrinkage rates are relatively balanced (usually 50%-70%), with good shrinkage uniformity, able to adapt to products with complex shapes (such as gift boxes, special-shaped parts).
- Fit: Tightly fits the product after shrinkage, without wrinkles or bubbles, and is one of the materials with the best fitting effect currently.
- Transparency: Extremely high transparency and good gloss, which can clearly display the product appearance and enhance the packaging grade (especially suitable for gifts and cosmetics).
- Advantages: Environmentally friendly and non-toxic (chlorine-free), resistant to low temperatures and impact, strong toughness after shrinkage, not easy to break, suitable for food contact packaging.
- Shrinkage Temperature: Relatively high, usually 120-180℃, requiring strong heating power (such as steam shrink machines or high-temperature hot air equipment).
- Shrinkage Rate: The shrinkage rate is low (longitudinal about 5%-15%, transverse about 30%-50%), and the shrinkage speed is slow, suitable for scenarios with low requirements for shrinkage amplitude (such as collective packaging).
- Fit: The fit is average, and it is relatively loose after shrinkage, more suitable for wrapping large or irregular products (such as furniture, building materials), mainly playing the role of fixing and dust prevention.
- Transparency: Low transparency (mostly translucent or milky white), poor gloss, not suitable for packaging that needs to display product details.
- Advantages: Strong puncture resistance and tear resistance, excellent toughness, suitable for outer protection of heavy products (such as barreled water, industrial parts).
- Shrinkage Temperature: High, about 130-180℃, and requires rapid heating (otherwise, incomplete shrinkage is prone to occur).
- Shrinkage Rate: Obvious unidirectional shrinkage (mostly transverse shrinkage, with extremely low longitudinal shrinkage rate), suitable for label shrinkage of cylindrical or columnar products (such as beverage bottles, cans) (i.e., "sleeve labeling").
- Fit: High fit for regular shapes (such as round, square bottle bodies), can tightly wrap the bottle body, not easy to fall off.
- Transparency: High transparency, good heat resistance (can withstand temperatures above 80℃), suitable for products that need high-temperature sterilization (such as bottled sauces).
- Limitations: Relatively brittle, poor impact resistance after shrinkage, and not suitable for products with complex shapes (easy to crack).
Shrinkage Uniformity
Materials with more stable molecular structures (such as POF) have more balanced force in all directions during shrinkage, resulting in flatter packaging;
Materials with obvious unidirectional shrinkage (such as PP) are only suitable for products with specific shapes, otherwise, local excessive shrinkage or insufficient shrinkage is likely to occur.
Temperature Adaptability
Low shrinkage temperature materials (PVC) will melt and break if heated by high-temperature equipment;
High shrinkage temperature materials (PE, PP) will shrink incompletely and fit loosely if heated insufficiently.
Product Compatibility
Brittle materials (PVC, PP) are not suitable for products with sharp edges and corners (easy to be scratched);
Tough materials (POF, PE) can adapt to complex shapes, but the low transparency of PE will obscure the product appearance.
Environmental Tolerance
PVC is easy to embrittle at low temperatures, and the packaging may crack after shrinkage;
POF and PE have good low-temperature resistance, suitable for cold chain transportation scenarios (such as frozen foods).