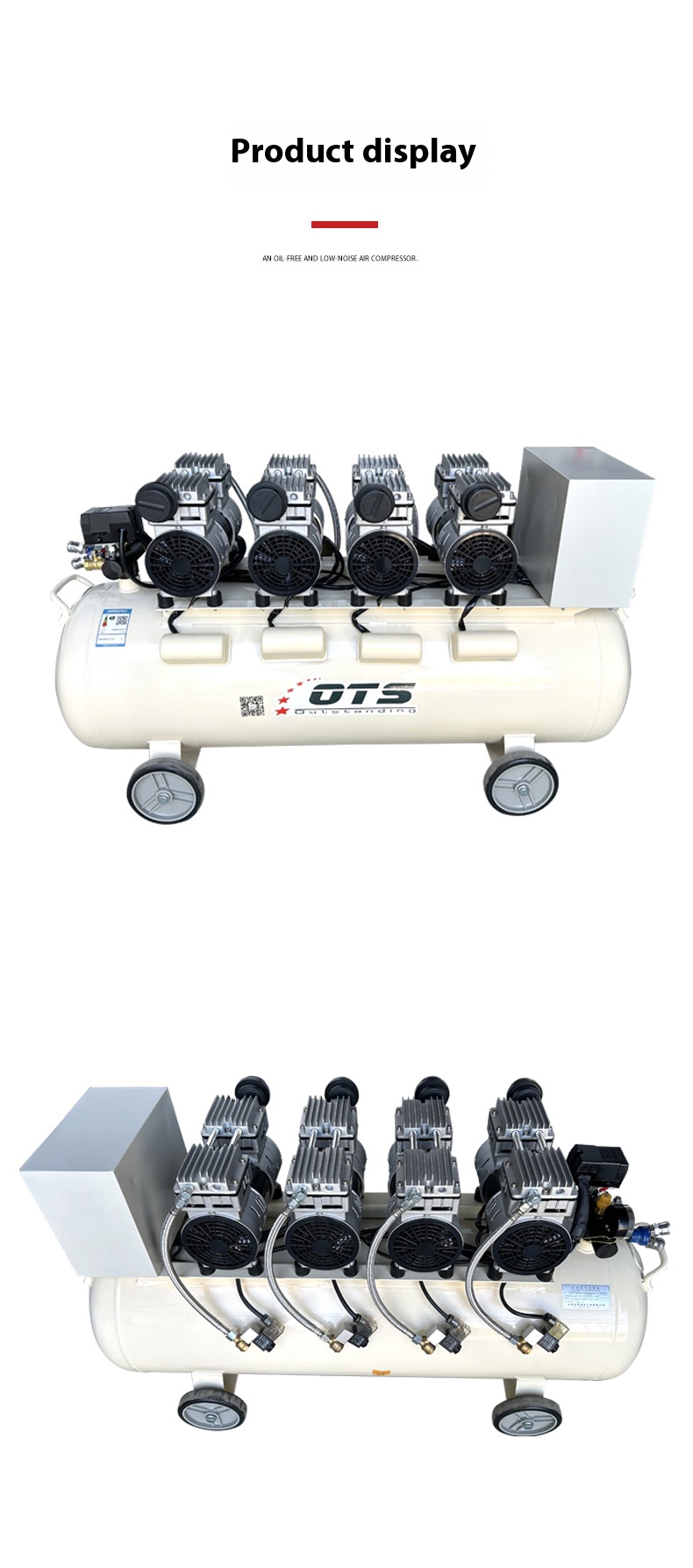
The core difference between oil-free air compressors and oil-lubricated air compressors lies in their lubrication methods, which gives rise to a series of disparities in compressed air cleanliness, structure, application scenarios, maintenance costs, and other aspects.
Oil-Free Air CompressorsNo lubricating oil is involved in the internal compression chamber. The operation of pistons/rotors is achieved by relying on self-lubricating materials (such as graphite, PTFE coatings, ceramic components) or water lubrication. The compressed air contains no oil mist or oil vapor, features high cleanliness, and can be directly used in scenarios requiring high gas purity.
Oil-Lubricated Air CompressorsLubricating oil serves as the medium for lubrication, sealing, and cooling. The lubricating oil will mix into the compressed air, which requires multi-stage treatment such as oil-gas separators and filters to remove oil content. However, trace amounts of oil mist may still remain (the oil content of conventional models is about 3–5 ppm, and that of high-efficiency filtration models can be reduced to 0.01 ppm).
Oil-Free Air CompressorsThey have a more complex structure, with the compression chamber completely isolated from the lubrication system. Some models (such as oil-free screw compressors) adopt a dry rotor design or are equipped with an independent water lubrication circuit. The components have higher material requirements (needing to be wear-resistant and self-lubricating).
Oil-Lubricated Air CompressorsThey have a relatively simple structure. Lubricating oil is directly injected into the compression chamber, serving both lubrication and sealing functions. The machining precision requirements for components are lower than those of oil-free models, resulting in lower manufacturing costs.
Oil-Free Air CompressorsSuitable for fields with stringent requirements for air cleanliness: food and beverage processing, pharmaceutical production, electronic chip manufacturing, medical respiratory equipment, pneumatic control systems for precision instruments, etc.
Oil-Lubricated Air CompressorsSuitable for industrial scenarios with no special requirements for oil content: driving pneumatic tools in machinery manufacturing workshops, mining rock drilling equipment, construction engineering pneumatic machinery, automobile maintenance, general factory production lines, etc.
Oil-Free Air CompressorsThere is no need to replace oil-gas separators, but it is necessary to regularly inspect the wear condition of self-lubricating components and replace the cooling medium (such as filtered water for water-lubricated models). The initial purchase cost is high, while the long-term maintenance cost is relatively stable, with no waste oil disposal costs.
Oil-Lubricated Air CompressorsIt is necessary to regularly replace lubricating oil, oil filters, and oil-gas separators, with a higher maintenance frequency. Moreover, the generated waste oil needs to be disposed of in compliance with regulations. The initial purchase cost is low, while the long-term cost of maintenance consumables is relatively high.
Oil-Free Air CompressorsDue to the lack of cooling effect from oil, the operating temperature is relatively high, and some models need to be equipped with a more powerful cooling system. Under the same power, the exhaust volume is slightly lower than that of oil-lubricated models.
Oil-Lubricated Air CompressorsThe cooling effect of lubricating oil results in lower operating temperature and higher energy efficiency. Under the same power, the exhaust volume is larger, and the operating noise is relatively lower.