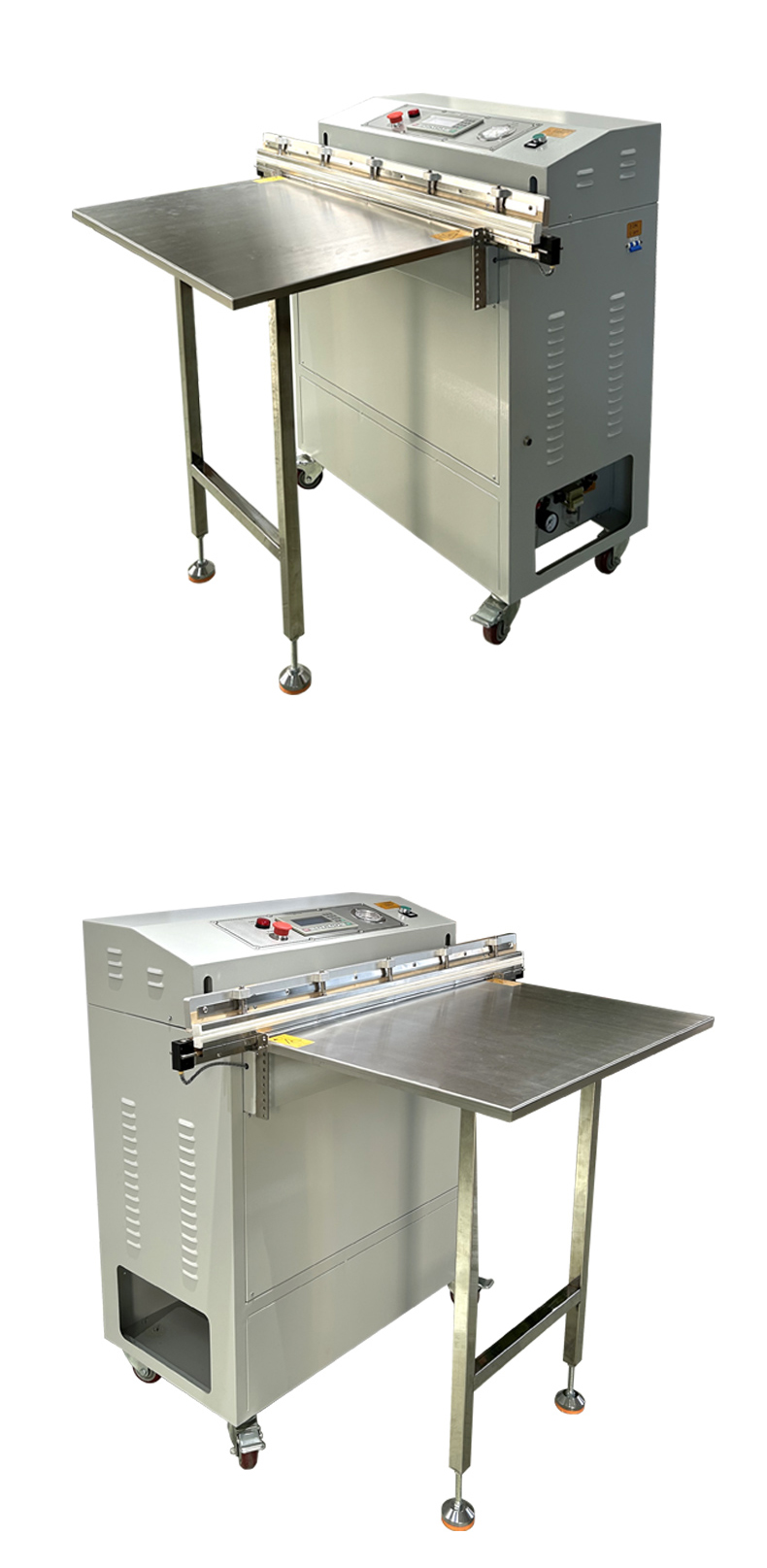
Common faults of pneumatic external vacuum packaging machines include insufficient vacuum degree, insecure or poor sealing, unstable operation of the equipment, and faults of the vacuum pump. The following are some common faults and their troubleshooting methods:
Insufficient Vacuum Degree
- Reasons: Insufficient vacuum pump oil or deteriorated oil quality; leakage at vacuum pipes or joints; blockage of the suction nozzle; poor sealing performance of the packaging bag.
- Solutions: Check the oil level of the vacuum pump and add or replace the vacuum pump oil; use soapy water or a leak detector to check the vacuum pipes and joints, and repair or replace the seals in time when a leakage point is found; clean the suction nozzle to ensure it is unobstructed; replace the packaging bag with good quality and excellent sealing performance.
Insecure or Poor Sealing
- Reasons: The sealing temperature is set too low or too high; the sealing time is too short or too long; there is dirt on the surface of the sealing strip or it is worn; insufficient air pressure.
- Solutions: Adjust the appropriate sealing temperature according to the material and thickness of the packaging bag; appropriately adjust the sealing time; clean the surface of the sealing strip, and replace the sealing strip if it is severely worn; check the air source pressure to ensure that the air pressure is stable and meets the equipment requirements.
Unstable Operation of the Equipment
- Reasons: Faults in the electrical control system; faults in pneumatic components; looseness or wear of mechanical parts.
- Solutions: Check the electrical circuit and control board, and replace the faulty components in time if any; check pneumatic components such as cylinders and solenoid valves, and repair or replace the damaged parts; tighten the loose mechanical parts and replace the severely worn parts.
Vacuum Pump Faults
- Reasons: The vacuum pump has not been maintained for a long time; motor faults; damage to the internal parts of the pump.
- Solutions: Regularly maintain the vacuum pump, such as replacing the machine oil and cleaning the filter; check whether the motor is powered on, and repair or replace the motor if there is a fault; open the vacuum pump to check the internal parts, such as the impeller and piston, and replace the damaged parts.
When troubleshooting faults, the operator should cut off the power supply and air source first to ensure safety. If encountering complex faults, it is recommended to contact professional maintenance personnel for handling to avoid greater losses